SNCR denitrification technology

SNCR (selective non catalytic reduction) denitrification technology is a kind of economical and practical NOx removal technology. Its principle is NH3, urea [CO (NH2) 2] as reductant, atomization or injection of heat in the boiler before the boiler is injected into the boiler. In the suitable temperature range, the ammonia or urea in the gas phase will be decomposed into free radicals NH3 and NH2. Under the condition of the specific temperature and oxygen, the reaction of reducing agent and NOx is better than other reactions. At a higher temperature range (850 ~1150 C), reducing agents (such as ammonia, CO or hydrocarbons) selectively reduced the NOx in the flue gas to N2 and water to reduce NOx emission.

The principle of SNCR denitrification
The principle of SNCR technology denitrification is:
In the range of 850~1100 C, the main reaction of NOx reduction by NH3 or urea is:
NH3 is a reductant:
4NH3+4NO+O2 - 4N2+6H2O
Urea is a reductant:
NO+CO (NH2) 2+1/2O2 to 2N2+CO2+H2O
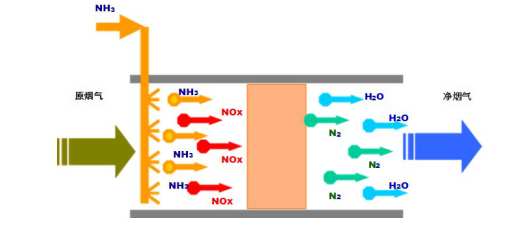
SNCR denitrification system consists of:
The SNCR denitrification system is mainly composed of ammonia (ammonia discharge, ammonia storage), reducing agent transportation system, measurement / distribution system, injection system, gas source station and control system.

The flue gas denitration process of SNCR system is completed by four basic processes.
Discharge and storage reducing agent;
The diluted reducing agent is injected into the proper position of the boiler.
The measuring output of reducing agent is mixed with water.
The reductant is mixed with the flue gas for the denitrification reaction.
